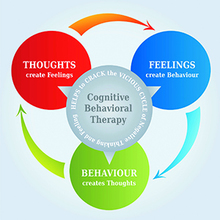
Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) is the most popular psychological treatment for mental health problems. So what is cognitive behaviour therapy and what are some of the CBT techniques used by practitioners? This article will provide a brief overview of CBT and of the techniques used to improve mental health.
What is cognitive behaviour therapy?
Based on CBT, the way we think (cognitions) affects how we feel and how we behave. The goal of treatment is therefore to identify a person’s thoughts and challenge or change them so that they become more realistic and helpful. For example, if we think that we are a failure, then this will make us feel down and depressed. This may result in us not trying very hard to do something, leading to an increased likelihood of failure. This failed attempt then reinforces our ‘self-failure’ belief.
Cognitive behaviour therapists often refer to the ABC model to help identify maladaptive thinking patterns and behaviours.
The goal in CBT is to identify thoughts and help clients to change them. Thoughts are often challenged and ‘thinking errors’ are identified. For example a person may have a tendency to fall into ‘magnification/minimisation’ traps. That is, they magnify the negatives about themselves, others or the world and minimise the positives.
CBT is an effective treatment for mental health problems and is often recommended as the primary treatment for depression and anxiety. It is by far the most popular treatment utilised by psychologists and other mental health practitioners.
Many people do benefit from many CBT techniques, however, it works best as part of an integrative approach.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.